FAQ:NewInstanceMsSql Linux: Difference between revisions
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Generalties== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{Warning | | {{Warning | Before anything, don't go further if you don't have read the first section [[General:Concepts|"dbSQWare Concepts "]] !}} | ||
=== | In this chapter, we will consider that SQWareCentral has been installed on dbsqware@sqwarebox. | ||
<br> | ===Limits of this section=== | ||
This chapter only deals with adding a new instance to a base that is already configured and functional.<br> | |||
Use the portions that apply to your environment, and choose either the automatic or manual method as desired<br> | |||
===General operating procedure for integrating a new Sql-Server instance=== | |||
There is only the case of remote connection to handle. We make an SQL connection from mssql@sqwarebox via FreeTds (OpenSource TDS connection client). | |||
Classic steps: | |||
*Setting up the environment | |||
*Manual tests | |||
*Deployment of the instance | |||
You will see that these steps can be handled one by one or in batches! | |||
== | ==Integration of an SQL-server instance== | ||
===Setting up the environment=== | |||
== | ====General==== | ||
=== | =====Explanation of "DbAlias" (the unique dbSQWare key)===== | ||
The dbSQWare key must be unique and must match the entry configured in the freetds.conf file to connect to the instance. | |||
Generally, when there is no named instance, we use the name of the Windows host that holds the instance. When there is a named instance, we concatenate the name of the Windows host and the instance name, separated by an underscore (do not use a backslash, we are on Linux!)."<br/> | |||
Examples : | |||
*WINMSQ => WINMSQ (status ON/LINUX) | *WINMSQ => WINMSQ (status ON/LINUX) | ||
*WINMSQ\INST1 => WINMSQ_INST1 (status ON/LINUX) | *WINMSQ\INST1 => WINMSQ_INST1 (status ON/LINUX) | ||
===== | =====Explanation of statuses===== | ||
Classically, for SQL Server, the status is 'ON'<br/> | |||
The 'OFF' status makes the instance disappear from the web view.<br/> | |||
The 'NEW' status is used as an intermediate status between the beginning and the end of setting up a new instance.<br/> | |||
All other statuses allow the instance to be displayed in the repository (especially 'KEEP'), but they will not be taken into account by the automatic processes."<br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Resume of statuses :<br/> | |||
{| align="center" {{Prettytable}} | {| align="center" {{Prettytable}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Statut''' | | '''Statut''' | ||
| '''Description''' | | '''Description''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| LINUX | | LINUX | ||
| | | locale instance(under Unix only) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| KEEP | | KEEP | ||
| | | temporary status, during maintenance for example or before complete deletion | ||
|- | |- | ||
| NEW | | NEW | ||
| | | temporary status, during configuration | ||
|- | |- | ||
| NEW_LINUX | | NEW_LINUX | ||
| | | temporary status, during configuration (under Unix only) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| OFF | | OFF | ||
| | | visual removal of the instance (without deleting its configuration) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXX | | XXX | ||
| | | not supported... | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== | ====Instance declaration in SQWareRepository with SQWareWeb==== | ||
We will declare the new instance from the SQWareWeb administration interface.<br/> | |||
[[ | [[File:Admin dbSQWare.png||admin|Admin dbSQWare]] | ||
<br/> | |||
Declare the new instance with the status "NEW" (Add or Duplicate).<br/> | |||
[[ | [[File:AjoutInstance.png||admin|Ajout d'une instance]] | ||
[[ | [[File:DuplicateInstance.png||admin|Ajout par duplication d'une instance]]<br/> | ||
[[ | [[File:DeclarationInstanceMsSqlLinux.png|admin|Add a new instance by duplicate an other one.]]<br/> | ||
Explanation of the fields :<br/> | |||
{| align="center" {{Prettytable}} | {| align="center" {{Prettytable}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ''' | | '''Fields''' | ||
| '''Description''' | | '''Description''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Db Alias | | Db Alias | ||
| | | Unique key that identifies the instance in dbSQWare (no value for MySQL/MariaDB). | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Dbms Name | | Dbms Name | ||
| Type | | Type of SGBD | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Virtual Host | | Virtual Host | ||
| Host | | Virtual Host (same as Host if not clustered) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Host Name | | Host Name | ||
| Hostname | | Hostname of the instance | ||
|- | |- | ||
| User Name | | User Name | ||
| User | | User associated with the instance | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Port | | Port | ||
| | | Listening port of the instance. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Comments | | Comments | ||
| | | A brief description of what the instance hosts | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Status | | Status | ||
| Instance | | Instance status (see above for explanations). | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Contact | | Contact | ||
| | | A contact if needed | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Environnement | | Environnement | ||
| | | Instance environment (PRD, PPR, REC, DEV, TST, ...) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Client | | Client | ||
| | | Used only for filtering (enter a client name and/or department and/or service...) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| GlobalHost | | GlobalHost | ||
| | | Free field in which the hypervisor host is often entered, for example. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Custom1 | | Custom1 | ||
| | | Free field 1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Custom2 | | Custom2 | ||
| | | Free field 2 | ||
|} | |} | ||
===== | =====Regenerate the reference files of SQWareCentral.===== | ||
Type the following command which will generate the reference files: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
| Line 131: | Line 133: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== | ====Verification of system prerequisites for the "local" part (bash + rsync)==== | ||
Since SQWareProduction is mainly written in bash shell and synchronized from SQWareCentral using rsync, we therefore need "bash" and "rsync" to be installed ! | |||
SQWareProduction | |||
===== | =====Verification===== | ||
Adapt to your username and machine name.<br> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
bash: | bash: | ||
| Line 144: | Line 143: | ||
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host | # From : mssql@my_mssql_host | ||
type bash | type bash | ||
# | #or | ||
which bash | which bash | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 151: | Line 150: | ||
# mssql@my_mssql_host | # mssql@my_mssql_host | ||
type rsync | type rsync | ||
# | #or | ||
which rsync | which rsync | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=====Installation===== | =====Installation===== | ||
Adapt to your machine type (use sudo if you are not root).<br/> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
RedHat / CentOS / ... : | RedHat / CentOS / ... : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line># From : root@my_mssql_host | ||
# From : root@my_mssql_host | |||
yum install -y bash rsync | yum install -y bash rsync | ||
# | #or | ||
dnf install -y bash rsync | dnf install -y bash rsync</syntaxhighlight> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Ubuntu / Debian / ... : | Ubuntu / Debian / ... : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : root@my_mssql_host | # From : root@my_mssql_host | ||
apt install -y bash rsync | apt install -y bash rsync | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Deployment of SSH key(s) from SQWareCentral to the target machine(s)==== | ||
There are two ways to proceed: | |||
* | *An automatic one (from dbsqware@sqwarebox, but it requires you to know the password of the mssql Unix account) | ||
* | *A manual one that you apply on each mssql Unix account | ||
/!\ | /!\ The password of your mssql Unix account must have been initialized, otherwise key-based authentication will not work! | ||
===== | =====Deployment of SSH key(s): batch method===== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
menu_msq GenDeplSshKeys_SQWareCentral GenLstInstanceNew | menu_msq GenDeplSshKeys_SQWareCentral GenLstInstanceNew | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Verify that this is indeed the list you want to deploy, then choose option 1 ...<br/> | |||
=> | => Enter the Unix password when prompted ! | ||
===== | =====Deployment of SSH key(s): manual method===== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host | # From : mssql@my_mssql_host | ||
| Line 198: | Line 195: | ||
chmod 600 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys | chmod 600 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=> | => Put the correct key in the "echo" (the one from dbsqware@sqwarebox) | ||
==== | ====SSH connection test from SQWareCentral==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
menu_msq TestSshConnection GenLstInstanceNew | menu_msq TestSshConnection GenLstInstanceNew | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
====Test | |||
====Test of prerequisites on the target host (bash+rsync) via SSH from SQWareCentral==== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
| Line 211: | Line 209: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Deployment of SQWareProduction==== | ||
Deployment of generic scripts and those specific to SQL Server in the $HOME of the user specified in SQWareRepository, for example mssql.<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | |||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
menu_msq DeplScripts GenLstInstanceNew | menu_msq DeplScripts GenLstInstanceNew | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Adding the dbSQWare environment to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile==== | ||
Once again, there are two ways to proceed: | |||
* | *An automatic one (from dbsqware@sqwarebox) | ||
* | *A manual one that you apply on each mssql Unix account | ||
===== | =====Adding the dbSQWare environment: batch method===== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
menu_msq AdddbSQWareProfile GenLstInstanceNew | menu_msq AdddbSQWareProfile GenLstInstanceNew | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Check that this is indeed the list you want to deploy, then choose 1 ...<br/> | |||
=> | => In ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile, change the following variable with the appropriate value: gvsqw_Env='XXX' | ||
===== | =====Adding the dbSQWare environment: manual method===== | ||
Add the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host | # From : mssql@my_mssql_host | ||
| Line 247: | Line 243: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===== | =====Adding the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable===== | ||
''' | '''Regardless of the method used:''' add the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host | # From : mssql@my_mssql_host | ||
| Line 254: | Line 250: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Creating the Connection to the SQL Instance==== | ||
/!\ | You have two options for connecting dbSQWare to your SQL Server instances: | ||
* Creating an SQL account within the instance requires that mixed login be enabled. | |||
* Using a service account (declared in Active Directory). | |||
=====Creating a Specific dbSQWare SQL Server Account===== | |||
/!\ SQL access must be authorized on the instances if it is not already enabled!<br/> | |||
Example creation order : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sql" line> | ||
USE [master] | USE [master] | ||
| Line 265: | Line 265: | ||
GO | GO | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
'sysadmin' | 'sysadmin' is mandatory, particularly because of the commands "DBCC". | ||
You can use any username and password you like!<br/> | |||
This account must be registered under the Unix account mssql@sqwarebox...<br/> | |||
If a specific entry is found, it will be used; otherwise, the "DEFAULT" entry will be used.<br/> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
mssql@ | mssql@sqwarebox:/home/mssql (NoSID) $ cat .passwd_mssql | ||
DEFAULT;msq_dba;NePasMettreCePassword! | DEFAULT;msq_dba;NePasMettreCePassword! | ||
SPECIFIC_MSSQL;sa;sapass | SPECIFIC_MSSQL;sa;sapass | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
====Test sendmail ( | =====Creating a connection with a specific dbSQWare service account===== | ||
Example of creation order : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql" line> | |||
USE [master] | |||
GO | |||
CREATE LOGIN [domain\svc-dbsqware] FROM WINDOWS; | |||
GO | |||
EXEC master..sp_addsrvrolemember @loginame = N'domain\svc-dbsqware', @rolename = N'sysadmin' | |||
GO | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The 'sysadmin' account is mandatory, particularly due to the "DBCC" commands.<br/> | |||
<br/> | |||
This account must be registered under the Unix account mssql@sqwarebox... <br/> | |||
If a specific entry is found, it is used; otherwise, the "DEFAULT" entry is used.<br/> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | |||
mssql@sqwarebox:/home/mssql (NoSID) $ cat .passwd_mssql | |||
DEFAULT;domain\svc-dbsqware;DoNotSetThisPassword! | |||
SPECIFIC_MSSQL;sa;sapass | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
====Test sendmail (not mandatory)==== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
| Line 282: | Line 302: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== | ===Manual Connection Tests to the SQL Server Instance=== | ||
/!\ | /!\ Only instances that will be in "LINUX" status! | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
| Line 289: | Line 309: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
== | ==Instance deployment== | ||
=== | ===Generating the default SQLwareProduction configuration=== | ||
/!\ | /!\ Only instances that will be in "LINUX" status! | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
| Line 297: | Line 317: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== | ===Updating SQWareRepository=== | ||
In the dbSQWare repository via the administration console, update the status of the new SQL Server instance (currently NEW_LINUX) to '''LINUX'''. | |||
=== | ===Testing the "recovery" of indicators=== | ||
At this point, you can test the recovery of missing indicators (generally, only the instances you just integrated!). | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | # From : dbsqware@sqwarebox | ||
## | ## For status "LINUX" | ||
repind_msq | repind_msq | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===Exploitation (stats, backups, …) | ===Exploitation (stats, backups, …) LINUX statuses === | ||
==== | ====Generating SQWareProduction Configurations==== | ||
If you followed the instance insertion procedure, this part is already done by the step "menu_msq GenDefConf_SQWareProduction GenLstInstanceNew".<br/> | |||
You can verify this in the following chapter.<br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> Connect to the central point's Unix machine with the "mssql" account and type the following commands:<br/> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
# From | # From mssql@vmsqwarebox | ||
#Enter the instance name | |||
too | |||
./sqwmsq_GenerateCreateInstance.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Verify that the proposed option is correct and type "y" if it is.<br/> | |||
At this point, you have generated the default configuration files for SQWareProduction. | |||
====Explanations==== | |||
The previous steps created some default files. ($HOME/admin/WINMSQ_INST1/sqwConfig) | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
#Enter the instance name | |||
# | |||
e WINMSQ_INST1 | e WINMSQ_INST1 | ||
cfg | cfg | ||
| Line 366: | Line 378: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
This is a configuration file used by the sqwmsq_RunJob.ksh script to execute actions.<br/> | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
File for a default cron job: $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
## mm(0-59) hh(0-23) dd(1-31) MM(0-12) DAY(0-sunday, 1-monday, ...) command | ## mm(0-59) hh(0-23) dd(1-31) MM(0-12) DAY(0-sunday, 1-monday, ...) command | ||
| Line 380: | Line 392: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Setting the backup path==== | ||
Backup test with master : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
#From mssql@ | #From mssql@vmsqwarebox | ||
$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_BackupDatabase.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -D master -Type full -Exec | $gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_BackupDatabase.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -D master -Type full -Exec | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
/!\ | /!\ Be careful with this part; if you're not sure, don't do anything : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
#From mssql@ | #From mssql@vmsqwarebox pour passer toutes les databases en 'RECOVERY SIMPLE' | ||
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseRecoverySimple.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | $gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseRecoverySimple.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | ||
#From mssql@ | #From mssql@vmsqwarebox pour modifier l'autogrowth toutes les logs de % en Mo | ||
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseModifyLogGrowth.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | $gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseModifyLogGrowth.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | ||
#From mssql@ | #From mssql@vmsqwarebox faire un SHRINK de toutes les logs | ||
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseShrinkLogs.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | $gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseShrinkLogs.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Deployment==== | ||
Setting up the cron : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
crontab -l > $HOME/CrontabRef | |||
vi $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 | vi $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 | ||
cat $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 >> $HOME/CrontabRef | cat $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 >> $HOME/CrontabRef | ||
| Line 410: | Line 423: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Updating the CrontabRef file : | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sh" line> | ||
crontab -l > $HOME/CrontabRef | crontab -l > $HOME/CrontabRef | ||
| Line 416: | Line 429: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== | ====Useful commands==== | ||
Interesting aliases : | |||
e DBALIAS => | e DBALIAS => Load the environment for the instance | ||
bin, etc, too ... => | bin, etc, too ... => To navigate to the standard SQWareProduction directory | ||
cbin, cetc, ctoo ... => | cbin, cetc, ctoo ... => To navigate to the custom SQWareProduction directory | ||
log => logs SQWareProduction | log => logs SQWareProduction | ||
Some script options : | |||
-h => | -h => online help | ||
-s => | -s => online examples | ||
-Exec => | -Exec => when present, executes the commands; if not set, only shows the commands without executing them. | ||
Examples : | |||
mssql@ | mssql@HOSTCENTRAL:$HOME/admin/WINMSQ_INST1/logs/StatisticsDatabase (WINMSQ_INST1) $ bin | ||
total 112 | total 112 | ||
drwxr-x--- 2 dbsqware dba 4096 Sep 25 21:22 . | drwxr-x--- 2 dbsqware dba 4096 Sep 25 21:22 . | ||
| Line 439: | Line 452: | ||
... | ... | ||
mssql@ | mssql@HOSTCENTRAL:$HOME/SQWareProduction/mssql/bin (WINMSQ_INST1) $ | ||
./sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh -h | ./sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh -h | ||
Latest revision as of 15:51, 8 December 2025
Generalties
In this chapter, we will consider that SQWareCentral has been installed on dbsqware@sqwarebox.
Limits of this section
This chapter only deals with adding a new instance to a base that is already configured and functional.
Use the portions that apply to your environment, and choose either the automatic or manual method as desired
General operating procedure for integrating a new Sql-Server instance
There is only the case of remote connection to handle. We make an SQL connection from mssql@sqwarebox via FreeTds (OpenSource TDS connection client).
Classic steps:
- Setting up the environment
- Manual tests
- Deployment of the instance
You will see that these steps can be handled one by one or in batches!
Integration of an SQL-server instance
Setting up the environment
General
Explanation of "DbAlias" (the unique dbSQWare key)
The dbSQWare key must be unique and must match the entry configured in the freetds.conf file to connect to the instance.
Generally, when there is no named instance, we use the name of the Windows host that holds the instance. When there is a named instance, we concatenate the name of the Windows host and the instance name, separated by an underscore (do not use a backslash, we are on Linux!)."
Examples :
- WINMSQ => WINMSQ (status ON/LINUX)
- WINMSQ\INST1 => WINMSQ_INST1 (status ON/LINUX)
Explanation of statuses
Classically, for SQL Server, the status is 'ON'
The 'OFF' status makes the instance disappear from the web view.
The 'NEW' status is used as an intermediate status between the beginning and the end of setting up a new instance.
All other statuses allow the instance to be displayed in the repository (especially 'KEEP'), but they will not be taken into account by the automatic processes."
Resume of statuses :
| Statut | Description |
| LINUX | locale instance(under Unix only) |
| KEEP | temporary status, during maintenance for example or before complete deletion |
| NEW | temporary status, during configuration |
| NEW_LINUX | temporary status, during configuration (under Unix only) |
| OFF | visual removal of the instance (without deleting its configuration) |
| XXX | not supported... |
Instance declaration in SQWareRepository with SQWareWeb
We will declare the new instance from the SQWareWeb administration interface.

Declare the new instance with the status "NEW" (Add or Duplicate).

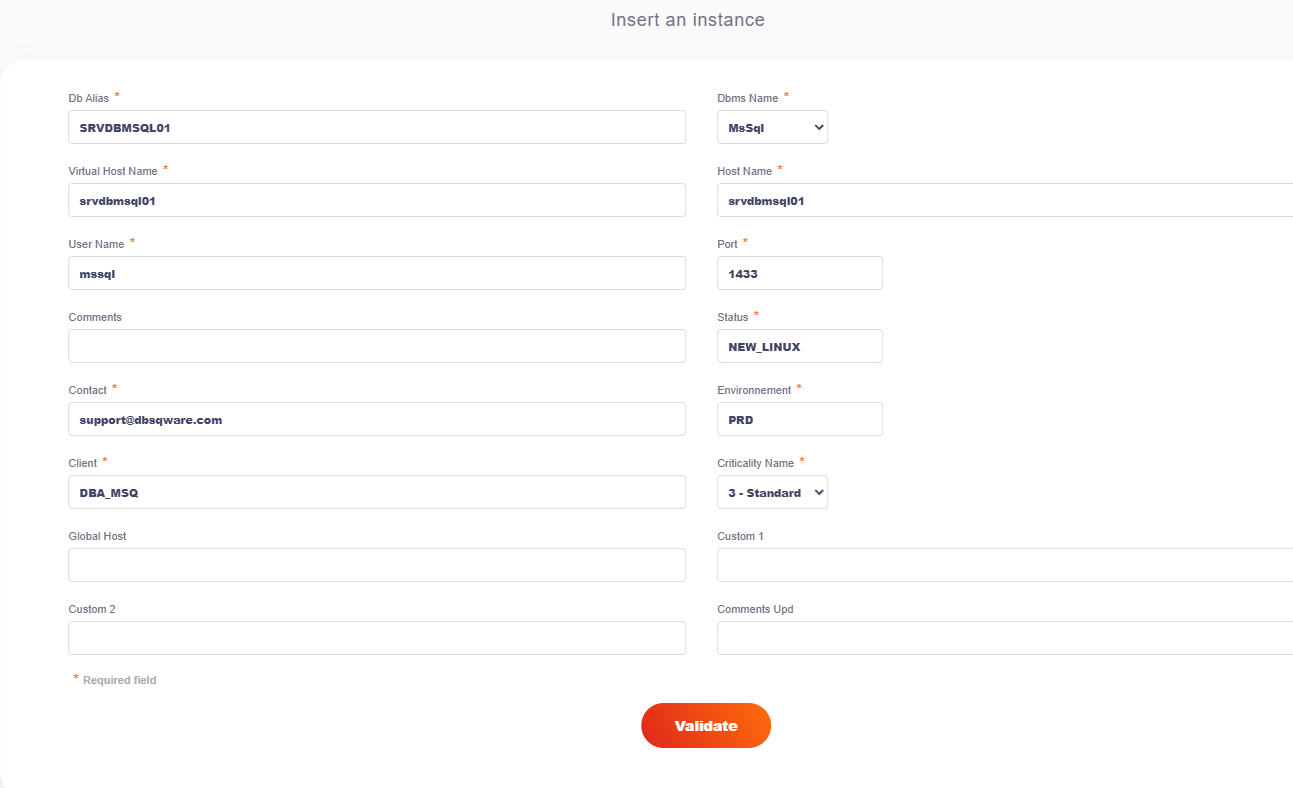
Explanation of the fields :
| Fields | Description |
| Db Alias | Unique key that identifies the instance in dbSQWare (no value for MySQL/MariaDB). |
| Dbms Name | Type of SGBD |
| Virtual Host | Virtual Host (same as Host if not clustered) |
| Host Name | Hostname of the instance |
| User Name | User associated with the instance |
| Port | Listening port of the instance. |
| Comments | A brief description of what the instance hosts |
| Status | Instance status (see above for explanations). |
| Contact | A contact if needed |
| Environnement | Instance environment (PRD, PPR, REC, DEV, TST, ...) |
| Client | Used only for filtering (enter a client name and/or department and/or service...) |
| GlobalHost | Free field in which the hypervisor host is often entered, for example. |
| Custom1 | Free field 1 |
| Custom2 | Free field 2 |
Regenerate the reference files of SQWareCentral.
Type the following command which will generate the reference files:
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
gen_all
Verification of system prerequisites for the "local" part (bash + rsync)
Since SQWareProduction is mainly written in bash shell and synchronized from SQWareCentral using rsync, we therefore need "bash" and "rsync" to be installed !
Verification
Adapt to your username and machine name.
bash:
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host
type bash
#or
which bash
rsync:
# mssql@my_mssql_host
type rsync
#or
which rsync
Installation
Adapt to your machine type (use sudo if you are not root).
RedHat / CentOS / ... :
# From : root@my_mssql_host
yum install -y bash rsync
#or
dnf install -y bash rsync
Ubuntu / Debian / ... :
# From : root@my_mssql_host
apt install -y bash rsync
Deployment of SSH key(s) from SQWareCentral to the target machine(s)
There are two ways to proceed:
- An automatic one (from dbsqware@sqwarebox, but it requires you to know the password of the mssql Unix account)
- A manual one that you apply on each mssql Unix account
/!\ The password of your mssql Unix account must have been initialized, otherwise key-based authentication will not work!
Deployment of SSH key(s): batch method
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq GenDeplSshKeys_SQWareCentral GenLstInstanceNew
Verify that this is indeed the list you want to deploy, then choose option 1 ...
=> Enter the Unix password when prompted !
Deployment of SSH key(s): manual method
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host
if [ ! -r $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa ]
then
ssh-keygen -t rsa -N '' -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
fi
chmod go-w $HOME
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB......XSPpdV11 dbsqware@sqwarebox" >>$HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 700 $HOME/.ssh
chmod 600 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
=> Put the correct key in the "echo" (the one from dbsqware@sqwarebox)
SSH connection test from SQWareCentral
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq TestSshConnection GenLstInstanceNew
Test of prerequisites on the target host (bash+rsync) via SSH from SQWareCentral
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq TestSysPrerequisites GenLstInstanceNew
Deployment of SQWareProduction
Deployment of generic scripts and those specific to SQL Server in the $HOME of the user specified in SQWareRepository, for example mssql.
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq DeplScripts GenLstInstanceNew
Adding the dbSQWare environment to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile
Once again, there are two ways to proceed:
- An automatic one (from dbsqware@sqwarebox)
- A manual one that you apply on each mssql Unix account
Adding the dbSQWare environment: batch method
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq AdddbSQWareProfile GenLstInstanceNew
Check that this is indeed the list you want to deploy, then choose 1 ...
=> In ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile, change the following variable with the appropriate value: gvsqw_Env='XXX'
Adding the dbSQWare environment: manual method
Add the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host
#dbSQWare
export gvsqw_MsqBin=$HOME/SQWareProduction/mssql/bin
export gvsqw_Env='PRD'
lvsqw_IsTerminal=$(tty 2>&1 >/dev/null;echo $?)
if [ "$lvsqw_IsTerminal" = "0" ] && [ -r $gvsqw_MsqBin/../etc/.profile_confort ]
then
. $gvsqw_MsqBin/../etc/.profile_confort
fi
Adding the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable
Regardless of the method used: add the lvsqw_InstanceParam variable to ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profile
# From : mssql@my_mssql_host
export lvsqw_InstanceParam=MSSQL_INST1
Creating the Connection to the SQL Instance
You have two options for connecting dbSQWare to your SQL Server instances:
- Creating an SQL account within the instance requires that mixed login be enabled.
- Using a service account (declared in Active Directory).
Creating a Specific dbSQWare SQL Server Account
/!\ SQL access must be authorized on the instances if it is not already enabled!
Example creation order :
USE [master]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [msq_dba] WITH PASSWORD=N'NePasMettreCePassword!', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=OFF, CHECK_POLICY=OFF
GO
EXEC master..sp_addsrvrolemember @loginame = N'msq_dba', @rolename = N'sysadmin'
GO
'sysadmin' is mandatory, particularly because of the commands "DBCC".
You can use any username and password you like!
This account must be registered under the Unix account mssql@sqwarebox...
If a specific entry is found, it will be used; otherwise, the "DEFAULT" entry will be used.
mssql@sqwarebox:/home/mssql (NoSID) $ cat .passwd_mssql
DEFAULT;msq_dba;NePasMettreCePassword!
SPECIFIC_MSSQL;sa;sapass
Creating a connection with a specific dbSQWare service account
Example of creation order :
USE [master]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [domain\svc-dbsqware] FROM WINDOWS;
GO
EXEC master..sp_addsrvrolemember @loginame = N'domain\svc-dbsqware', @rolename = N'sysadmin'
GO
The 'sysadmin' account is mandatory, particularly due to the "DBCC" commands.
This account must be registered under the Unix account mssql@sqwarebox...
If a specific entry is found, it is used; otherwise, the "DEFAULT" entry is used.
mssql@sqwarebox:/home/mssql (NoSID) $ cat .passwd_mssql
DEFAULT;domain\svc-dbsqware;DoNotSetThisPassword!
SPECIFIC_MSSQL;sa;sapass
Test sendmail (not mandatory)
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq TestSendmail GenLstInstanceNew
Manual Connection Tests to the SQL Server Instance
/!\ Only instances that will be in "LINUX" status!
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq TestInstConnectionOnNoMail GenLstInstanceNew
Instance deployment
Generating the default SQLwareProduction configuration
/!\ Only instances that will be in "LINUX" status!
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
menu_msq GenDefConf_SQWareProduction GenLstInstanceNew
Updating SQWareRepository
In the dbSQWare repository via the administration console, update the status of the new SQL Server instance (currently NEW_LINUX) to LINUX.
Testing the "recovery" of indicators
At this point, you can test the recovery of missing indicators (generally, only the instances you just integrated!).
# From : dbsqware@sqwarebox
## For status "LINUX"
repind_msq
Exploitation (stats, backups, …) LINUX statuses
Generating SQWareProduction Configurations
If you followed the instance insertion procedure, this part is already done by the step "menu_msq GenDefConf_SQWareProduction GenLstInstanceNew".
You can verify this in the following chapter.
Connect to the central point's Unix machine with the "mssql" account and type the following commands:
# From mssql@vmsqwarebox
#Enter the instance name
too
./sqwmsq_GenerateCreateInstance.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1
Verify that the proposed option is correct and type "y" if it is.
At this point, you have generated the default configuration files for SQWareProduction.
Explanations
The previous steps created some default files. ($HOME/admin/WINMSQ_INST1/sqwConfig)
#Enter the instance name
e WINMSQ_INST1
cfg
cat sqwmsq_Jobs.cfg
#############################################
#IndicDba: Gather DBAs indicators
IndicDba:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_GatherIndicators.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1
#RotateErrorLog: Rotate error log
RotateErrorLog:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RotateErrorLog.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#BackupAll: backup all databases
BackupAll:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_BackupAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#BackupAllRep: run failed backups from BackupAll
BackupAllRep:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_BackupAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -REP -Exec
#StatisticsAll : update statistics tables for all databases
StatisticsAll:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#RebuildAll : Rebuild indexes tables for all databases
RebuildAll:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RebuildIndexAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#RestoreParfile : restore list of databases content in parfile
RestoreParfile:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RestoreAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -PAR $Parfile -Exec
#CheckdbAll : DBCC CheckDB for all databases
CheckdbAll:$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_CheckdbAllDatabases.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
This is a configuration file used by the sqwmsq_RunJob.ksh script to execute actions.
File for a default cron job: $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 :
## mm(0-59) hh(0-23) dd(1-31) MM(0-12) DAY(0-sunday, 1-monday, ...) command
## WINMSQ_INST1
# Backup all databases
00 22 * * 1-6 bash -c '. $HOME/.profile ;$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RunJob.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -A BackupAll > $HOME/tmp/BackupAll_WINMSQ_INST1.log 2>&1'
# Rebuild all databases
30 07 * * 6 bash -c '. $HOME/.profile ;$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RunJob.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -A RebuildAll > $HOME/tmp/RebuildAll_WINMSQ_INST1.log 2>&1'
# Stats all databases
00 07 * * 0 bash -c '. $HOME/.profile ;$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_RunJob.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -A StatisticsAll > $HOME/tmp/StatisticsAll_WINMSQ_INST1.log 2>&1'
Setting the backup path
Backup test with master :
#From mssql@vmsqwarebox
$gvsqw_MsqBin/sqwmsq_BackupDatabase.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -D master -Type full -Exec
/!\ Be careful with this part; if you're not sure, don't do anything :
#From mssql@vmsqwarebox pour passer toutes les databases en 'RECOVERY SIMPLE'
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseRecoverySimple.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#From mssql@vmsqwarebox pour modifier l'autogrowth toutes les logs de % en Mo
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseModifyLogGrowth.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
#From mssql@vmsqwarebox faire un SHRINK de toutes les logs
$gvsqw_MsqBin/../tools/sqwmsq_AlterDatabaseShrinkLogs.ksh -I WINMSQ_INST1 -Exec
Deployment
Setting up the cron :
crontab -l > $HOME/CrontabRef
vi $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1
cat $HOME/CrontabRef_WINMSQ_INST1 >> $HOME/CrontabRef
vi $HOME/CrontabRef
crontab $HOME/CrontabRef
crontab -l
Updating the CrontabRef file :
crontab -l > $HOME/CrontabRef
cat $HOME/CrontabRef
Useful commands
Interesting aliases :
e DBALIAS => Load the environment for the instance bin, etc, too ... => To navigate to the standard SQWareProduction directory cbin, cetc, ctoo ... => To navigate to the custom SQWareProduction directory log => logs SQWareProduction
Some script options :
-h => online help -s => online examples -Exec => when present, executes the commands; if not set, only shows the commands without executing them.
Examples :
mssql@HOSTCENTRAL:$HOME/admin/WINMSQ_INST1/logs/StatisticsDatabase (WINMSQ_INST1) $ bin total 112 drwxr-x--- 2 dbsqware dba 4096 Sep 25 21:22 . drwxr-x--- 15 dbsqware dba 4096 Sep 25 21:22 .. -rwxr-x--- 1 dbsqware dba 10858 Sep 25 21:22 sqwmsq_BackupAllDatabases.ksh -rwxr-x--- 1 dbsqware dba 6013 Sep 25 21:22 sqwmsq_BackupDatabase.ksh -rwxr-x--- 1 dbsqware dba 7663 Sep 25 21:22 sqwmsq_CheckdbAllDatabases.ksh -rwxr-x--- 1 dbsqware dba 4809 Sep 25 21:22 sqwmsq_CheckdbDatabase.ksh ...
mssql@HOSTCENTRAL:$HOME/SQWareProduction/mssql/bin (WINMSQ_INST1) $
./sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh -h
Sourcing sqwmsq_Global.lib v2021.02 SQWareProduction for MsSql ...
Usage: sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh [-h] -S|-I <FreeTdsAlias> [+ options]
DESCRIPTION
sqwmsq_StatisticsAllDatabases.ksh update Statistics databases in //
SUPPORT
MsSql supported versions: 2000 <= v <= 2019
PARAMETERS
-S|-I Instance : Target instance (freeTds alias).
OPTIONS
-h help : Display the full usage.
-s : Display samples of usage.
-P Nb_threads : Number of threads in parallel (by default 4).
-ID listdb : Databases list to include.
-ED listdb : Databases list to exclude.
-IL likeclause : Like clause to generate databases list (example: 'db%').
-EL likeclause : Like clause to exclude databases (example: 'nodb%').
-WCD whereclause : Where clause to generate databases list.
-FRT return_code : Force return code value on error.
-AddMail email : Email Address to add at 'xxx'.
-SendReport : Send execution log report.
-PAR parfile : Parfile file for databases list.
-AGR Nb_sec : Nb of seconds between two run (by default 5s).
-AGE Nb_sec : Nb of seconds between two check of end (by default 5s).
-NoMail : Desactivate sendmail on error xxx (by default, send on error).
-Exec : Execute commands (default, display generated commands)
Enjoy !
